3.2 Study 2: Cross-national survey on consumers food risk management quality evaluations
Aims
- To identify the factors influencing consumer evaluations of food risk management practices
- To model those factors to provide a useful instrument for gaining a better understanding of how consumer view food risk management practices
- To examine the extent to which these factors differ among different European member states (cross-cultural variation)
Implications
The results of this study will provide insights for the development of more effective and trusted food risk management strategies, and will indicate whether implementation of a single European policy regarding food risk management strategies is feasible.
Methodology
| How? | Internet Questionnaire (except Slovenia) + Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) |
| Where? | Greece |
| Denmark | |
| Slovenia | |
| UK | |
| Germany | |
| How many participants? | 2533 |
The researched countries have been selected based on Hofstede value.
In the focus groups (Study 1), consumers and experts gave their opinion on food risk management. From those discussions, some topics were found to be important regarding consumers’ evaluations of food risk management practices and were converted into relevant items used in the consumer survey. In the survey, the participants had to say if they agreed or not with the items on the questionnaire.
The following figure shows some examples of items:
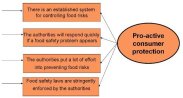
After analysing all the data collected from the questionnaire, a model of consumer attitudes was created. It lists the factors that influence how people evaluate food risk management practices. In addition, the importance of these factors and the differences between the five countries is shown.
Results
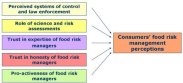
This survey showed that consumers’ evaluations of food risk management practices are dependent on several factors, which are shown in the figure below:
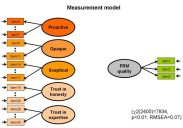
With data obtained from the survey, a measurement model was created and later on validated. The measurement model shows how the items and the constructs are related.
The constructs that seemed to influence food risk management quality are shown in the Measurement model, they are:
- Proactive consumer protection
- Opaque and reactive risk management
- Scepticism in risk assessment and risk communication practices
- Trust in expertise of food risk managers
- Trust in honesty of food risk managers
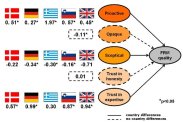
The Structural model demonstrates how the constructs are related to Food Risk Management quality.
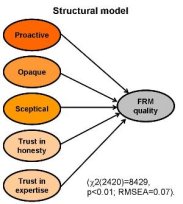
Some other results from the survey are illustrated in the next figure. It explains how the constructs affect the Food Risk Management quality. The constructs 'Opaque' and 'Trust in honesty' both had the same effect in all the 5 countries were the survey took place. However, only in the case of 'Opaque' this effect was significant. In contrast, the three other constructs had a different effect in the 5 countries and all are significant except the effect of 'Trust in expertise' in Greece.
For example, 'Proactive' has a different positive effect on food risk management in each country. This implies that proactive consumer protection contributes to a positive evaluation of the quality of food risk management practices, but this effect is more prominent in Greece than in Germany. On the other hand, 'Opaque' has a negative effect in all countries. This means that when there is an opaque risk management, this is damaging for food risk management quality.
In summary, factors of universal importance related to food risk management quality evaluations:
- Pro-active consumer protection
- Opaque and reactive risk management
- Trust in the expertise of food risk managers (except Greece)
And factors of local importance related to food risk management quality evaluations:
- Scepticism in risk assessment and communication practices
Implications for food risk management
From these results, practical recommendations can be formulated, which can immediately be applied in the area of food risk management.
For communication:
- Provide the right consumers with the right information through the right source
For management:
- Provide proactive communication about various factors inherent to risk management and risk assessment
- Incorporate the views and opinions of all stakeholders in the process of risk analysis
Understand consumer concerns.
